Python in Web Development
INTRODUCTION:
Python web development is a popular and adaptable option for creating dynamic websites and web apps. A wide range of frameworks, modules, and tools are available for Python, which makes development easier and enables programmers to design scalable and effective web solutions.
It comprises designing, developing, and maintaining websites with a range of functions and uses by utilizing a variety of technologies, programming languages, and tools.
At its foundation, web development includes two essential aspects:
1. Front-end development
2. Back-end development
Front-end Development:
The visual and interactive components of a website that visitors interact with directly are the focus of front-end development. Using tools like HTML (Hypertext Markup Language), CSS (Cascading Style Sheets), and JavaScript, entails developing the layout, designing the user interface (UI), and implementing the visual components.
Back-end Development:
On the other hand, back-end development works with a website’s server-side functionality. It entails developing the architecture and logic needed to process data, manage database interactions, and maintain the operation of the website. Programming languages like Python, Ruby, Java, or PHP are used by back-end developers to create the server-side parts of websites.
WEB DEVELOPMENT USING PYTHON:
The process of developing websites and web applications with the Python programming language is known as Python web development. Python is a widely used and adaptable programming language that is well-known for its ease of use, readability, and extensive library and framework ecosystem.
Python is used by developers to construct server-side logic for web applications. This involves processing HTTP requests and responses, data storage and retrieval, business logic implementation, and dynamic content rendering.
SEVERAL ADVANTAGES TO USE PYTHON IN WEB DEVELOPMENT:
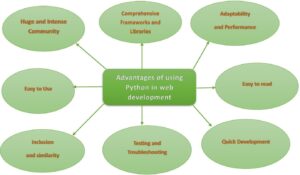
- Huge and Intense Community:
The Python community is large and vibrant, with many developers contributing to its development and providing assistance. Many tools, frameworks, and resources designed expressly for web development are available from the community. Python is a strong option for web development because of its wealth of community-driven tools and resources, which provide answers to a variety of needs.
- Comprehensive Frameworks and Libraries:
Python has a robust ecosystem of frameworks and tools that make web development chores easier. One of the most well-liked web frameworks for Python, Django, offers a sophisticated and comprehensive toolkit for creating intricate web applications. It is designed using the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architectural paradigm and comes pre-configured with features like URL routing, database ORM (Object-Relational Mapping), and authentication. Another lightweight and adaptable micro-framework that gives developers more control over the components and structure of an application is Flask. These frameworks, as well as others like Pyramid and Bottle, give web development a strong base and increase productivity.
- Adaptability and Performance:
Python is well-known for being performant and scalable, which makes it ideal for managing online applications with heavy traffic. Python frameworks like Django and asyncio can effectively manage concurrent requests and optimize server resources thanks to innovations like asynchronous programming. Furthermore, Python’s integration features make it simple to integrate with other languages, allowing programmers to use high-performance C or C++ libraries as necessary.
- Easy to read and use:
Python’s syntax is intended to be simple to understand and write, focusing on code readability and maintainability. Its simple syntax enables developers to express concepts in fewer lines of code, making development faster and more efficient. Python’s simplicity allows both new and experienced developers to work easily and collaboratively.
- Inclusion and Simplicity:
Python is adaptable for web development and interfaces with other technologies with ease. It supports a wide range of databases, including NoSQL databases like MongoDB and SQL-based databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQLite.
- Testing and Troubleshooting:
Python has strong testing frameworks that make developing and running tests for web applications easier, such unittest and pytest. Integrated development environments (IDEs) and pdb are two of the efficient debugging tools that enable developers to locate problems and solve them fast.
- Quick Development:
Python’s emphasis on productivity and simplicity makes it possible for developers to create web apps rapidly. Pre-built modules and libraries are readily available, allowing developers to take advantage of pre-existing solutions rather than having to start from scratch. Time-to-market is critical for startups and small-scale ventures, where this speedy development strategy is very helpful.
WEB DEVELOPMENT FRAMEWORKS IN PYTHON:
Python offers several web frameworks to suit different needs and preferences. The following are a few well-known Python web development frameworks:
- Django
- Flask
- Pyramid
- Bottle
- CherryPy
- Tornado
WEB DEVELOPMENT LIBRARIES IN PYTHON:
Python web development provides an abundance of tools and frameworks to improve productivity and improve the development process. The following libraries & tools are frequently used in Python web development:
- Jinja2
- Pydantic
- Redis-py
- PyJWT
- Flask-WTF
- Flask-SQLAlchemy
- Celery
- SQLAlchemy
- Pillow
- Beautiful Soup
- Requests
ROADMAP FOR PYTHON WEB DEVELOPMENT:
A road map for using Python to construct websites that highlights the main ideas and procedures involved:
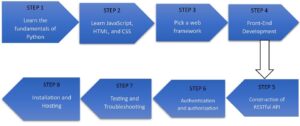
- Learn the fundamentals of Python:
Learn the syntax, data types, control structures, and functions that are essential to Python programming. To begin started, you can consult books or internet guides.
- Learn JavaScript, HTML, and CSS:
Get a fundamental knowledge of web technologies, like JavaScript for client-side interactivity, CSS for styling, and HTML for markup. These are required to understand and design websites.
- Pick a web Framework:
Choose a Python web framework based on the needs of your project. A few well-liked choices are Pyramid, Flask, and Django.
- Front-end Development:
Develop your web development abilities by being familiar with well-known front-end frameworks and modules like Angular, Vue.js, and React.
- Construction of RESTful API:
Create APIs that provide data and functionality to other apps or front-end interfaces using the web framework of your choice.
- Authentication and Authorization:
Learn how to use the built-in capabilities or extensions of your web framework to develop secure user registration, login, and access control techniques.
- Testing and Troubleshooting:
Become an expert at testing your websites. Find out more about end-to-end, integration, and unit testing. To write and run tests, use tools such as pytest, Python’s Selenium, or the testing frameworks included with your preferred web framework.
- Installation and Hosting:
Find out how to put your web application on a cloud platform or web server. Gain an understanding of ideas like scalability, security considerations, deployment automation, and server setup. For hosting web applications, platforms like Heroku, AWS, or PythonAnywhere are frequently utilized.
CONCLUSION:
Python is a powerful language that is well-suited for web development, which involves developing websites and web apps. Because of its ease of use, readability, and robust environment, Python is a great option for web development projects. Python offers a strong basis for web development, making it possible for programmers to create feature-rich, scalable websites quickly.
How to Get Ready for a Python Interview
Python has become one of the most popular programming languages, and its widespread use in a variety of industries has resulted in an increased demand for skilled Python developers.
Getting ready for a Python interview requires technical preparation, problem-solving practice, and strategic planning. Here’s a step-by-step guide that will help you prepare effectively.
Understand the Job Requirements:
Begin by carefully reviewing the job description and requirements. Determine the key skills and technologies that the employer is looking for, and tailor your preparation accordingly.
Review Python Basics:
Make sure you understand the fundamental Python concepts, such as data types, loops, conditional statements, functions, and basic file operations. Prepare to write clean, efficient Python code.
Data Structures and Algorithms:
Brush up on basic data structures (lists, dictionaries, and sets) and algorithms. Practice coding challenges on platforms such as LeetCode, HackerRank, and CodeSignal. Concentrate on time and space complexity analysis.
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP):
Understand OOP concepts like encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism. Prepare to apply these concepts to real-world problems and explain their significance.
Python Libraries and Frameworks:
Familiarize yourself with Python libraries and frameworks that are relevant to your role. For example, if the job requires web development, learn about Flask or Django. If it involves data science, be familiar with Pandas, NumPy, and scikit-learn.
Database Knowledge:
Review basic SQL queries and learn how Python interacts with databases through libraries such as SQLAlchemy and Django ORM. Understand the differences between various database types and when to use them.
Web Technologies (if applicable):
If the job requires web development, brush up on your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript skills. Learn how Python integrates with front-end technologies and how to build RESTful APIs.
Testing and Debugging:
Practice with testing frameworks such as unittest and pytest. Be familiar with Python debugging tools and techniques like pdb. Recognize the significance of writing testable and debuggable code.
Version Control:
Refresh your understanding of Git and GitHub. Understand basic commands, branching strategies, and how to effectively collaborate with version control.
Soft Skills and Behavioral Questions:
Prepare for soft-skills and behavioral questions. Prepare to discuss your problem-solving approach, teamwork, communication skills, and previous experiences. To structure your responses, follow the STAR method (Situation, Task, Action, Result).
Mock Interviews:
Conduct mock interviews with a friend, mentor, or on online platforms that provide interview practice. To boost your confidence and communication skills, practice real-world interview scenarios.
Review Your Resume:
Prepare to discuss any past projects or experiences listed on your resume. Highlight your accomplishments, obstacles overcome, and the impact of your contributions.
Stay Updated:
Keep up with the latest Python development trends, updates, and best practices. Follow industry blogs, attend webinars, and join relevant forums.
Ask Questions:
Prepare thoughtful questions for the interviewer. This demonstrates your interest in both the company and the position. Questions about the team, projects, and corporate culture are frequently well received.
Final Preparations:
In the days leading up to the interview, review key concepts, practice coding challenges, and get plenty of sleep. Make sure you have a reliable internet connection and a quiet, well-lit environment for the virtual interview.
Remember, preparation is essential for success in a Python interview. Approach each question confidently, demonstrate your problem-solving abilities, and communicate clearly. Good luck!
Begin your Journey Today,
for Training, Contact via Call/WhatsApp :+91 90427 10472
Recent Posts
Categories
- All
- Angularjs training in Chennai
- ASP.NET Core
- dot net training
- dot net training in chennai
- dotnet full stack developer
- Free dotnet training
- information on dotnet
- Learn Java in chennai
- Learn Python at Karaikudi
- learn python online
- learn python online from chennai
- Linq Queries in .net
- mutual funds
- MVC Training Tutorials
- PHP Training in Chennai
- pmp training online
- power apps online training
- Python Training Online
- share market
- Sharepoint framework online training
- SharePoint Freelancers in Chennai
- software testing
- spfx online training
- Stock market
- Uncategorized
